The tasty and juicy mango has just got a shot in the arm. According to research, regular consumption of the fruit by obese adults may lower blood sugar levels and does not negatively impact body weight.
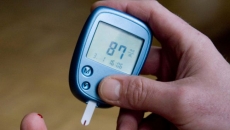
"Our results indicate that daily consumption of one half of a fresh mango (about 100 grams) may help lower blood sugar in obese individuals," said Edralin Lucas, an associate professor from the department of nutritional sciences at Oklahoma State University's college of human sciences.
Mangoes contain many bio-active compounds, including mangiferin, an antioxidant that contributes to the beneficial effects of mango on blood glucose.
"In addition, mangoes contain fibre which can help lower glucose absorption into the blood stream," Lucas added.
During the study, 20 adults aged 20 to 50 years with a Body Mass Index (BMI) of 30 to 45 consumed 10 grams of freeze-dried or dehydrated mango.
Their dietary intake was monitored via three-day food records assessed at baseline and after six and 12 weeks of mango supplementation.
Researchers found that after 12 weeks, participants had reduced blood glucose and this glucose lowering effect was seen in both males and females.
No changes were observed in overall body weight.
However, hip circumference was significantly lower in males but not females.
"We believe mangoes may give obese individuals a dietary option in helping them maintain or lower their blood sugar," Lucas added.
However, the precise component and mechanism has yet to be found and further clinical trials are necessary.
Mangoes are an excellent source of the anti-oxidant vitamins C and A as well as folate. They are also a good source of copper and vitamin B6.
The study appeared in the journal Nutrition and Metabolic Insights.