For the first time, Ebola has been discovered inside the eyes of a patient months after the virus was gone from his blood.
Ebola has infected more than 26,000 people since December 2013 in West Africa. Some survivors have reported eye problems but how often they occur isn't known. The virus also is thought to be able to persist in semen for several months.
The new report concerns Dr. Ian Crozier, a 43-year-old American physician diagnosed with Ebola in September while working with the World Health Organization in Sierra Leone.
He was treated at Emory University Hospital's special Ebola unit in Atlanta and released in October when Ebola was no longer detected in his blood. Two months later, he developed an inflammation and very high blood pressure in one eye, which causes swelling and potentially serious vision problems.
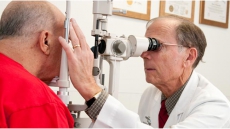
He returned to Emory, where ophthalmologist Dr. Steven Yeh drained some of the fluid and had it tested for Ebola. It contained the virus but tears and tissue around the outside of his eye did not.
That suggests that casual contact with an Ebola survivor poses no public health risk, but shows that survivors need to be monitored for the eye problem, Yeh said.
Crozier has not fully recovered his vision but continues to improve, Yeh said.
Dr. Jay Varkey, an Emory infectious disease specialist, said those involved in Crozier's care wore recommended protective gear and monitored themselves for Ebola symptoms for several weeks afterward as a precaution.
Doctors discussed the case at an Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology conference in Denver on Thursday, and the New England Journal of Medicine published their account online.
Earlier Thursday, the World Health Organization said that the number of Ebola cases reported in Guinea and Sierra Leone last week dropped to its lowest total this year. And Liberia, which has had the most deaths in the outbreak — more than 4,700 — plans on Saturday to declare the outbreak over in that country unless new cases are discovered.