NEW YORK — Health officials are trying to unravel how a relative may have picked up a Zika infection from a Utah man who died.
The tropical virus rarely spreads from person to person, not like the flu or the measles. The virus can pass from a pregnant woman to her fetus and cause birth defects. And it can also be spread through sex. But it is mostly spread by mosquitoes.
In the Utah case, health officials are looking for other explanations. Only the elderly man, who died in late June, had been in a country with a Zika outbreak — not the relative who had been caring for him.
HOW IS ZIKA USUALLY SPREAD?
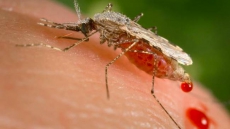
The bite of a mosquito. That's behind the large outbreaks in dozens of countries in Latin America and the Caribbean. It's the same mosquito — Aedes aegypti — that can spread other tropical diseases, like dengue fever, chikungunya and yellow fever. In fact, the bug was known as the yellow fever mosquito for many years.
HOW DOES THAT WORK?
It starts with a person who is infected with Zika. A female mosquito bites that person and drinks in blood, which it needs to make eggs. Then it spreads the virus when it bites another person nearby. Health officials don't think that's what happened in Utah; the Zika mosquito hasn't been seen in Salt Lake City. But it's theoretically possible that an infected mosquito returned with the elderly man from his trip abroad — perhaps in his suitcase — and bit the relative.

WHAT ABOUT BLOOD?
Zika can be spread through blood, but official stress that mosquito bites are the way most people are infected. There's been at least one instance of a lab worker who was accidentally infected through blood. The virus stays in the blood for about a week. The Food and Drug Administration has recommended that blood banks decline donations from people who have travelled to Zika areas within the previous month.
BUT, WHAT ELSE?
Evidence of Zika infection has been found in number of other body fluids, including saliva, urine, semen, vaginal fluid and even breast milk. Scientists have established that it's been spread through sex, mostly by men to their partners. Health officials say there's no evidence that Zika can be spread through coughing or sneezing or routine touching.

WHAT HAPPENED IN UTAH?
The elderly man had an extremely large amount of virus in his blood — the most ever seen. That helped make this case highly unusual, said officials at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Higher levels of virus in the blood can make someone more contagious.
His infection was only confirmed through tests after he died. He had another health condition, which health officials have not identified, and it is unclear if Zika played a role in his death. Disease detectives are investigating the possibility that the relative somehow caught it while caring for the elderly man at a home and in a hospital. The male relative had developed a mild Zika illness and quickly recovered. In most people, the virus causes a mild illness at worst.
Investigators are doing more interviewing and testing other family members and health-care workers who may have been in close contact with the man who died. They also are trapping local mosquitoes.